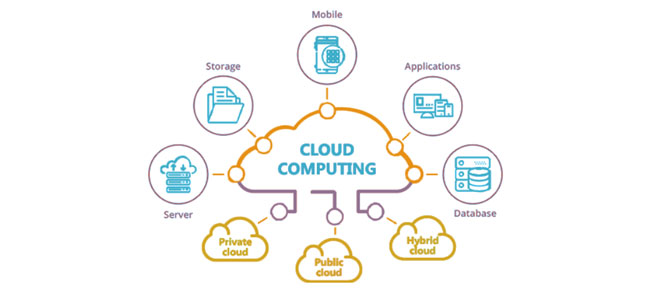
Cloud Technology
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. Instead of buying, owning, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you can access technology services, such as computing power, storage, and databases, on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure, GCP.
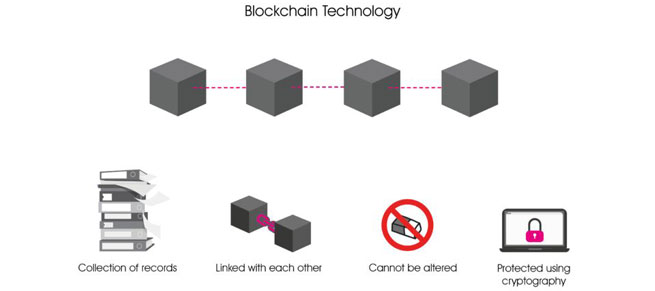
Blockchain Technology
A blockchain is a distributed database or ledger that is shared among the nodes of a computer network. As a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in digital format. Blockchains are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems, such as Bitcoin, for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions.
Blockchain is to allow digital information to be recorded and distributed, but not edited. In this way, a blockchain is the foundation for immutable ledgers, or records of transactions that cannot be altered, deleted, or destroyed.
IoT Applications
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects
embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, allowing them to
collect and exchange data over the internet. These "smart" devices can
range from everyday items like refrigerators and thermostats to complex
industrial machinery.
Key
Features:
Connectivity:
Devices within the IoT ecosystem are interconnected, enabling seamless
communication and data exchange.
Sensors and Data Collection:
IoT devices are equipped with sensors that gather real-time data,
providing valuable insights for analysis and decision-making.
Remote Monitoring and Control:
Users can monitor and control IoT devices remotely, enhancing
convenience and efficiency.

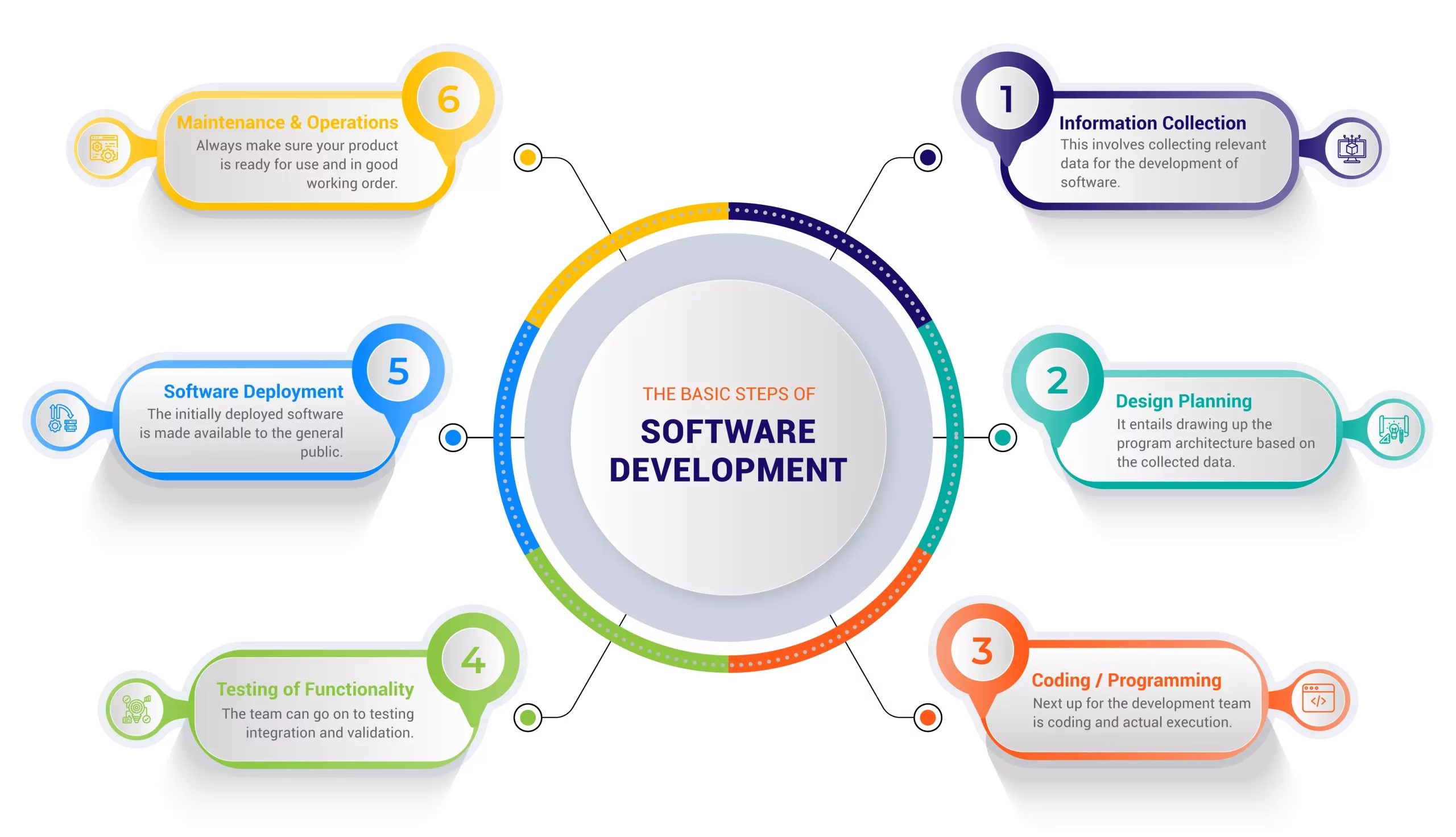
Application Development
Application development,
often referred to as app development, is the process of creating
software applications for mobile devices, desktops, web browsers, or
embedded systems. It involves a series of steps, from conceptualization
and design to coding, testing, and deployment.
Key Stages of
Application Development:
Planning and
Conceptualization:
Define the purpose, features, and target audience of the
application.
Design:
Create a user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design to ensure a
seamless and intuitive user journey.
Development:
Write the code that brings the application to life, considering factors
like scalability, security, and performance.
Testing:
Thoroughly test the application for functionality, usability, and
security to identify and resolve any issues.
Deployment:
Release the application to the intended platform, whether it's an app
store, a website, or an enterprise environment.
Maintenance and Updates:
Continuously monitor and update the application to fix bugs, improve
performance, and introduce new features.
